
The Changing Face of Urban Planning: LiDAR and Future Cityscapes
Urban planning and sustainable city development are paramount in our rapidly expanding world. As cities expand and evolve, innovative technologies such as LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) are being deployed to address complex challenges. LiDAR is a game-changer in urban planning, offering invaluable insights and data for shaping future cities. This technology is being used to create 3D models of cities and to gather real-time data that allows city planners to make informed decisions about urban development and to create smart cities that are resilient to future challenges.
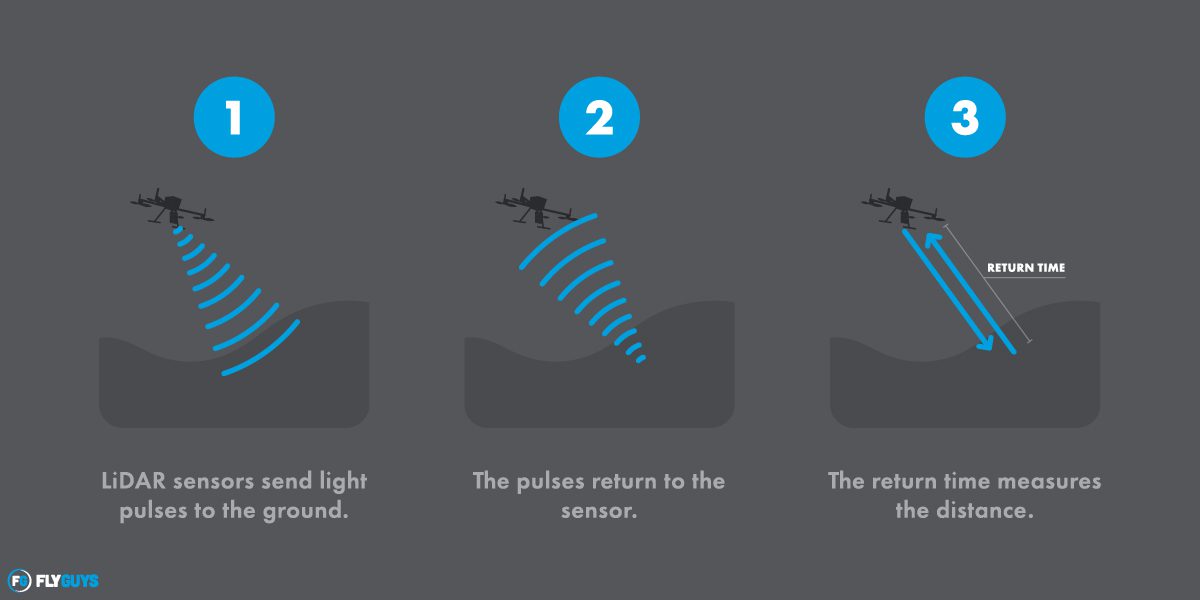
Understanding LiDAR Technology
LiDAR is a cutting-edge technology that employs laser pulses to measure distances and create precise 3D representations of objects and environments. Unlike traditional surveying methods, LiDAR enables rapid and accurate data collection in vast urban areas, capturing intricate details essential for informed decision-making.
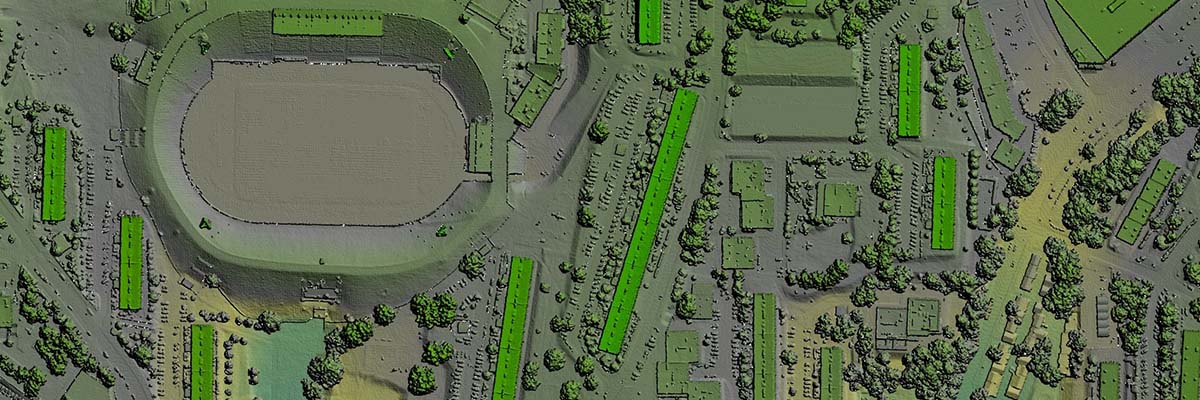

Creating Detailed Urban Models
3D city models generated by LiDAR are highly accurate and comprehensive. These models allow city planners and decision-makers to visualize, analyze, and plan the urban landscape more effectively. Professionals can optimize urban design and development by integrating LiDAR-derived data into their workflows. These high-fidelity representations empower city planners and decision-makers with information beyond traditional surveying methods.
Let’s look at some of the key advantages of LiDAR-derived 3D city models.
Accurate Geospatial Data: LiDAR systems capture precise measurements that ensure 3D models accurately reflect the real-world environment. Accuracy is vital for various applications, such as infrastructure design, environmental analysis, and transportation planning.
Time and Cost Efficiency: LiDAR technology can rapidly scan large regions, significantly reducing the time required to gather data. This efficiency translates into cost savings for projects, enabling planners to allocate resources more effectively and take on larger and more ambitious undertakings.
Seamless Integration with GIS and BIM: Providing a more holistic view of the city enhances data value. With GIS, planners can overlay additional layers of information, such as demographics and land use, enabling them to make more informed decisions. Streamlining the design and construction process is made easier with BIM integration.
Data-Driven Decision Making: City planners can rely on data-driven insights to assess various scenarios, test hypotheses, and simulate the impact of different development strategies. This evidence-based approach minimizes risks and increases urban project success.
Planning for Disaster Resilience: LiDAR-generated 3D city models help identify areas prone to flooding, landslides, or other hazards. By understanding the topography and terrain in detail, city planners can implement measures to minimize disaster impact and safeguard the city’s infrastructure and inhabitants.
Citizen Engagement and Public Participation: By providing accessible and visually compelling representations of proposed projects, city planners can effectively communicate their plans to the public, fostering trust, encouraging feedback, and allowing citizens to actively participate in shaping the future of their city.
Monitoring Urban Change: LiDAR technology allows for periodic updates of the 3D city models, facilitating the monitoring of urban changes and growth patterns. These insights provide vital data for assessing the effectiveness of previous urban development strategies and adjusting future plans accordingly.
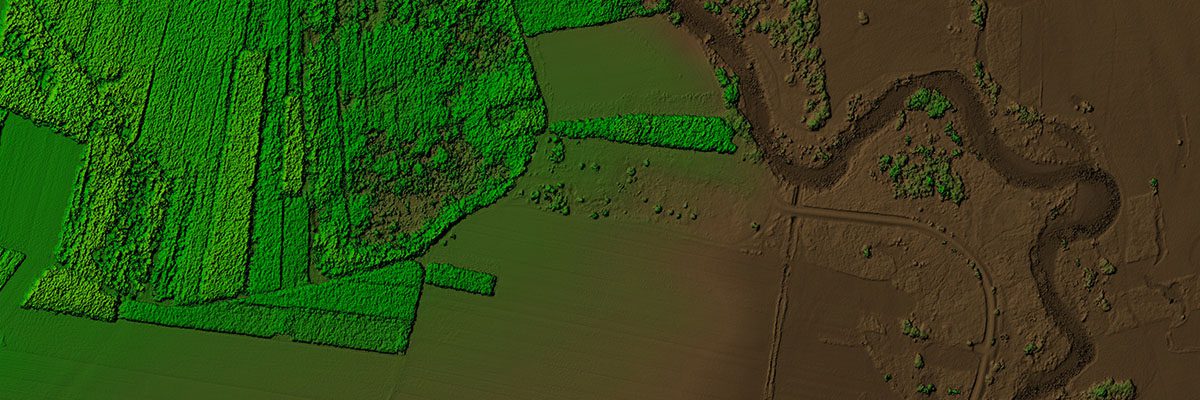

Identifying Potential Risks in Infrastructure
Safety and resilience are paramount in urban planning, and LiDAR is pivotal in infrastructure assessment and monitoring. LiDAR helps minimize risks and enhances disaster risk reduction and mitigation planning by pinpointing vulnerabilities in critical structures like buildings and bridges.
So how can LiDAR help identify potential risks and mitigate planning? Let’s find out.
Detailed Structural Assessments: LiDAR’s ability to capture high-resolution 3D data enables engineers and inspectors to conduct detailed structural assessments remotely. By analyzing the data, they can identify cracks, deformations, and other signs of deterioration that may not be easily visible to the naked eye.
Monitoring Structural Health: By performing periodic LiDAR scans, engineers can track structural changes and assess whether they are within acceptable limits. This data-driven approach allows for early detection of developing issues, enabling timely maintenance or intervention to prevent potential failures.
Detecting Environmental Impact: LiDAR data provides critical insights into the surrounding terrain and environmental factors that can impact infrastructure stability. For example, LiDAR can help assess flood risk by mapping flood-prone areas, allowing planners to take preventative measures in vulnerable regions.
Analyzing Load-Bearing Capacities: This information is invaluable in understanding how infrastructure will perform under various stress conditions, ensuring that they are designed and maintained to meet safety standards.
Disaster Risk Reduction and Mitigation: By generating detailed elevation models and flood simulations, LiDAR helps identify areas at higher risk of flooding or landslides, allowing for strategic land-use planning and appropriate protective measures.
After the devastating earthquake in Nepal in 2015, LiDAR technology was employed to assess the structural integrity of heritage sites and monuments. This data aided in prioritizing restoration efforts and ensuring the safety of tourists and locals visiting these historic landmarks.
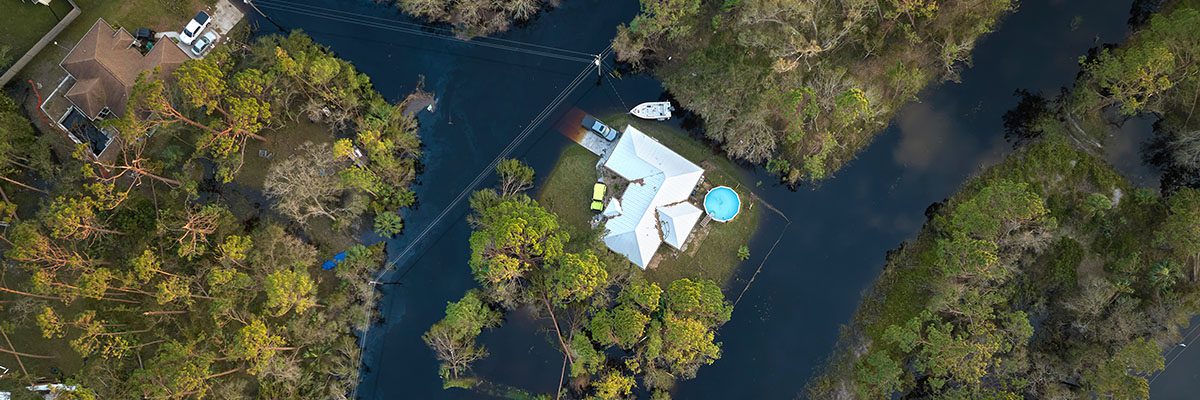

Designing Resilient Cities
Resilience is a critical concept in urban planning, focusing on a city’s ability to withstand and recover from shocks and stresses. By incorporating LiDAR data, cities can enhance their preparedness against climate change and extreme events.
Analyzing Potential Hazards: By analyzing the terrain and identifying vulnerable areas prone to flooding, landslides, or other natural hazards, cities can make informed decisions when planning new infrastructure or retrofitting existing structures.
Supporting Resilient Infrastructure: Engineers can use LiDAR data in the planning and design process that optimizes infrastructure projects to withstand the impacts of extreme events. This includes ensuring that critical infrastructure, such as bridges, roads, and utilities, is built with the necessary structural integrity and flexibility to cope with various stressors.
Enhancing Climate Change Preparedness: LiDAR data provides valuable insights into the topography, hydrology, and vegetation patterns, which are essential for understanding climate change impacts on urban areas. By identifying areas at risk of sea-level rise, urban heat island effects, or increased frequency of extreme weather events, cities can develop adaptation strategies to safeguard their communities and infrastructure.
Improving Disaster Response and Recovery: LiDAR-derived 3D models offer real-time situational awareness, enabling emergency responders to navigate affected areas more effectively and plan rescue operations efficiently. Additionally, these models aid in damage assessment and post-disaster recovery efforts, ensuring a quick return to normalcy.
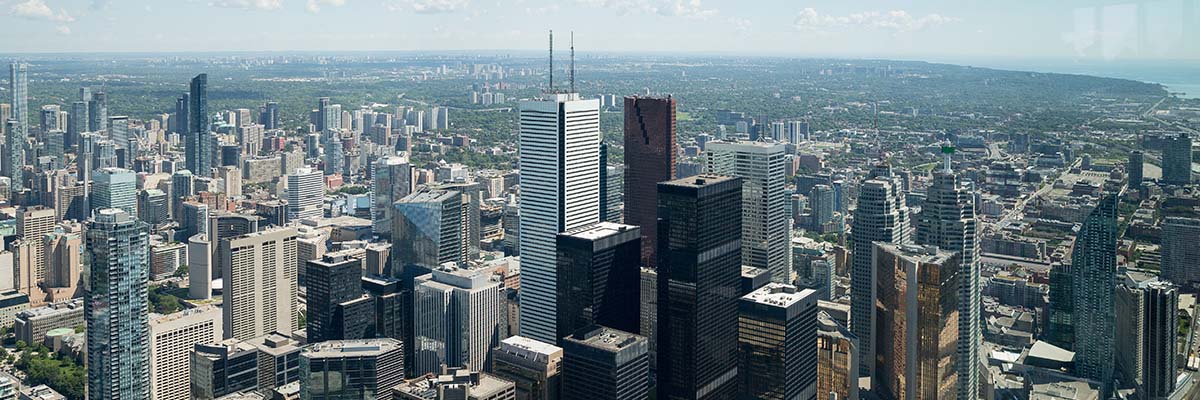

Fostering Sustainable Cities
Sustainability is a cornerstone of modern urban planning. LiDAR data analysis helps optimize energy efficiency, plan green spaces, and manage waste effectively. Successful cities have already embraced LiDAR to make significant strides toward sustainable urbanization.
One such city was Toronto, which used LiDAR data to address climate change challenges in three ways. The first focused on estimating stormwater flow using high-resolution LiDAR data, revealing how urban street features can significantly influence and direct water flows. The second use calculated the solar potential of different land parcels in the city, discovering that a substantial portion had excellent solar potential. The third use of LiDAR involved determining building heights and emergency response times for high-rise buildings, which showed that most buildings over 17 stories had a response time of 5 minutes or less for emergency services. ¹
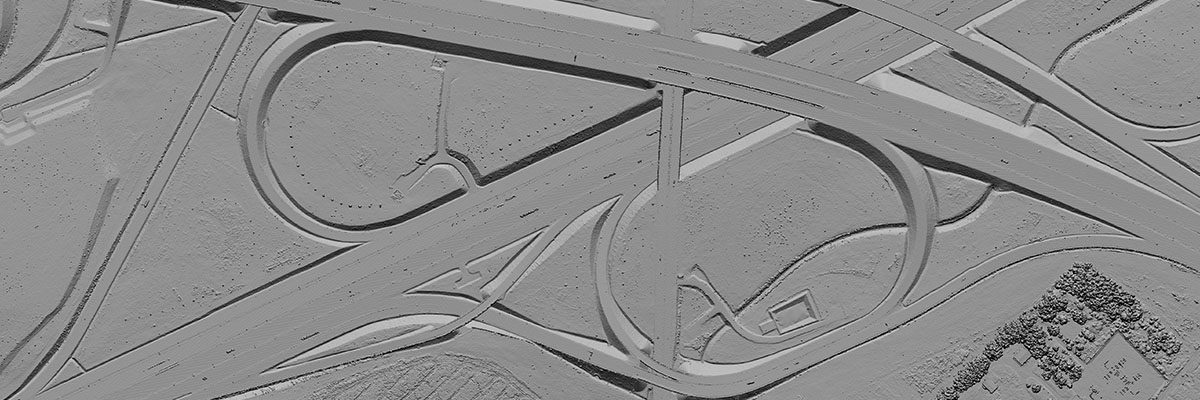

Overcoming Challenges and Ethical Considerations
As with any transformative technology, LiDAR faces challenges.
Integrating LiDAR into urban planning practices requires a significant initial investment in technology, data processing, and equipment. Cities must allocate resources to acquire LiDAR sensors and software for data analysis. Moreover, implementing LiDAR effectively demands skilled personnel who can operate the technology, process the vast amounts of data generated, and interpret the results accurately. Training existing staff or hiring specialized professionals adds to the challenges and costs of adoption.
LiDAR data is crucial, but it also raises privacy concerns. Cities must establish clear data governance policies to protect citizen privacy and ensure that data is used responsibly and ethically. Building public trust by being transparent about data collection and storage practices is essential for successful LiDAR adoption.
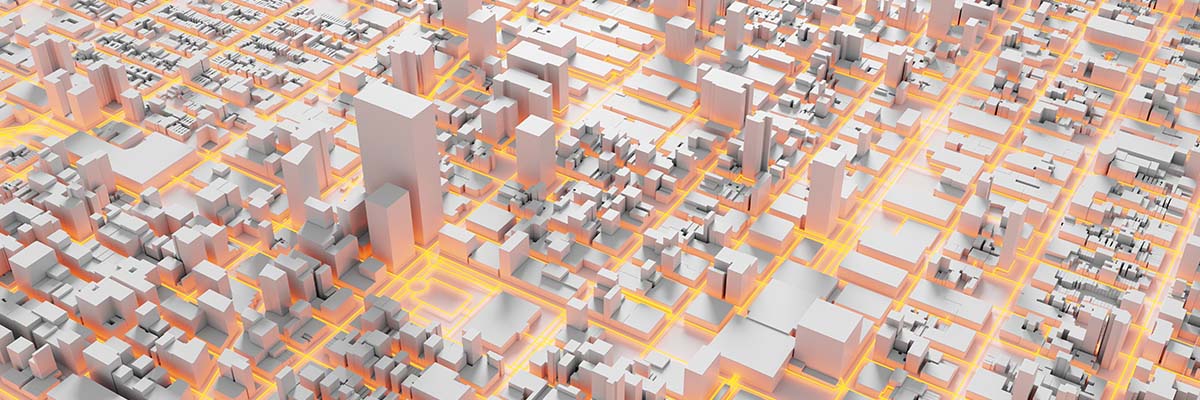

Future Implications and Innovations
The future of LiDAR in urban planning is promising, with continual advancements on the horizon. Improved data processing techniques and more cost-effective LiDAR systems will make it more accessible to cities of all sizes. Innovations such as simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) will enhance data accuracy and real-time applications.
LiDAR technology’s transformative impact on urban planning and city development cannot be overstated. From creating detailed 3D urban models to identifying risks, fostering resilience, and promoting sustainability, LiDAR offers an indispensable toolkit for city planners and engineers. As we embrace LiDAR and other innovative technologies, we hold the power to create better, more sustainable, and resilient cities for generations to come. It is up to city planners, policymakers, and citizens, to seize this opportunity and shape the future of our urban landscapes for the better. Embrace LiDAR, and together, let’s build the cities of tomorrow, today.
