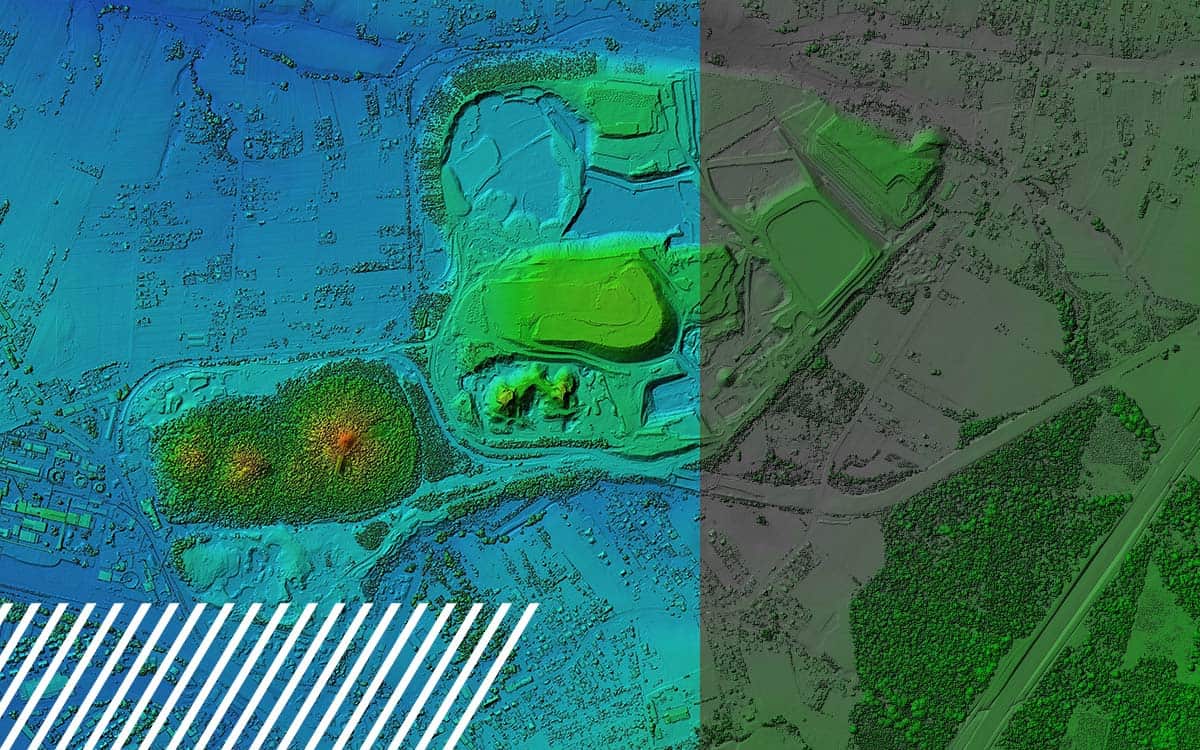
The Power of GIS in the Reality Data Capture Industry
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are revolutionizing the way industries collect, analyze, and utilize spatial data. As a critical component of reality data capture, GIS combines location-based data with advanced analytics to create meaningful insights. These insights drive better decision-making, improve operational efficiency, and unlock new opportunities for growth.
What is GIS?
GIS is a technology that captures, stores, analyzes, and visualizes data related to the Earth’s surface. It integrates diverse data sources—such as satellite imagery, drone data, LiDAR scans, and GPS measurements—to provide a comprehensive view of spatial environments. More than just mapping, GIS helps users interpret complex data sets, revealing patterns, relationships, and trends that would otherwise be hidden.
How GIS Enhances Reality Data Capture
In the reality data capture industry, GIS is indispensable. It provides the framework to organize, analyze, and share data efficiently. Here’s how it elevates our services:
Accurate Spatial Data Collection
GIS supports precise data collection using drones and sensors, ensuring high-resolution spatial information. This data is crucial for industries where accuracy directly impacts outcomes, such as construction, utilities, and environmental management.
Advanced Visualization
GIS allows for the creation of detailed 2D and 3D visualizations. These models enable stakeholders to understand site conditions, plan projects more effectively, and identify potential challenges before they arise.
Integrated Data Analysis
By layering data from multiple sources—such as topography, infrastructure, and vegetation—GIS provides a holistic view of an area. This integration helps industries make informed decisions based on comprehensive data sets.
Real-Time Monitoring and Updates
GIS facilitates real-time data integration, allowing for continuous monitoring of sites. For example, in agriculture, GIS helps monitor crop health, water usage, and soil conditions, enabling farmers to react promptly to changing conditions.
Predictive Analytics
GIS can analyze historical and current data to forecast future trends. Industries like energy and transportation use GIS to predict maintenance needs, optimize routes, and plan for growth.

Applications of GIS Across Industries
GIS technology is a game-changer for industries that rely on spatial data for decision-making and operations. By integrating data from various sources, GIS provides actionable insights that drive efficiency and innovation. Here’s a deeper look at how GIS is transforming key industries:
Agriculture
In modern agriculture, GIS is indispensable for improving productivity and sustainability.
- Precision Farming: Farmers use GIS to map fields, analyze soil properties, and monitor crop health. This enables precise application of water, fertilizers, and pesticides, reducing waste and costs.
- Crop Yield Analysis: By comparing historical data with real-time imagery, GIS helps predict crop yields and identify underperforming areas.
- Weather and Climate Monitoring: GIS integrates meteorological data to help farmers prepare for weather events and adapt to climate change.
- Irrigation Management: Efficient water usage is critical in agriculture. GIS helps design and monitor irrigation systems to optimize water distribution and prevent overuse.

Construction and Urban Planning
GIS is a cornerstone for planning and managing urban development and construction projects.
- Site Selection and Feasibility Studies: GIS helps evaluate potential sites by analyzing topography, soil conditions, zoning laws, and proximity to infrastructure.
- Infrastructure Design and Modeling: Engineers and architects use GIS to create 3D models of buildings, roads, and utilities, ensuring designs fit the landscape and meet regulatory standards.
- Project Monitoring: GIS enables real-time tracking of construction progress, helping stakeholders stay on schedule and within budget.
- Risk Assessment: By analyzing environmental and geological data, GIS identifies risks such as flood zones, landslides, or earthquake-prone areas, enabling proactive mitigation strategies.
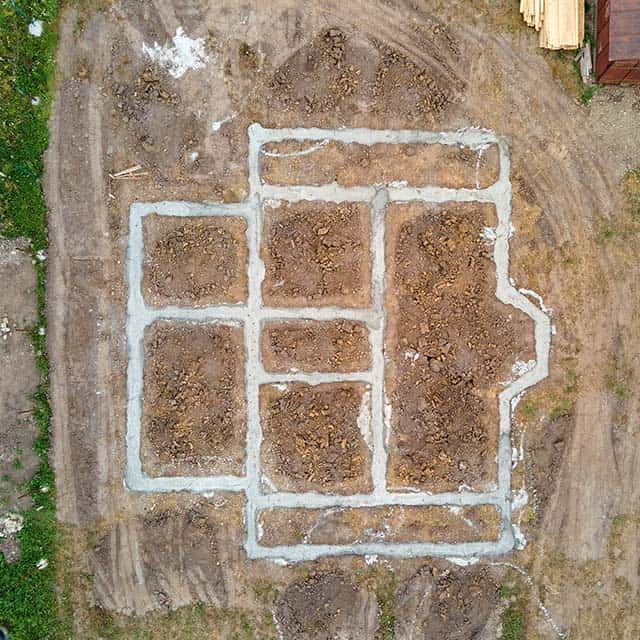

Environmental Management
GIS is critical for monitoring and managing natural resources and ecosystems.
- Deforestation Tracking: GIS helps map and monitor deforestation, providing data to enforce regulations and support reforestation efforts.
- Wildlife Conservation: By tracking animal movements and habitat changes, GIS supports conservation programs and helps mitigate human-wildlife conflicts.
- Water Resource Management: GIS monitors water bodies for pollution, assesses water availability, and plans sustainable usage.
- Disaster Management: GIS aids in predicting and responding to natural disasters such as floods, wildfires, and hurricanes by modeling risk areas and tracking events in real time.

Transportation and Logistics
GIS enhances the efficiency and safety of transportation systems and supply chains.
- Route Optimization: GIS analyzes traffic patterns, road conditions, and delivery points to optimize routes, reducing fuel costs and delivery times.
- Infrastructure Planning: Planners use GIS to design and maintain transportation networks, from highways to public transit systems, ensuring connectivity and efficiency.
- Safety Analysis: GIS identifies high-risk areas for accidents, enabling authorities to implement safety measures such as better signage or road improvements.
- Supply Chain Management: By visualizing logistics networks, GIS helps businesses streamline operations, manage inventory, and respond to disruptions in real time.

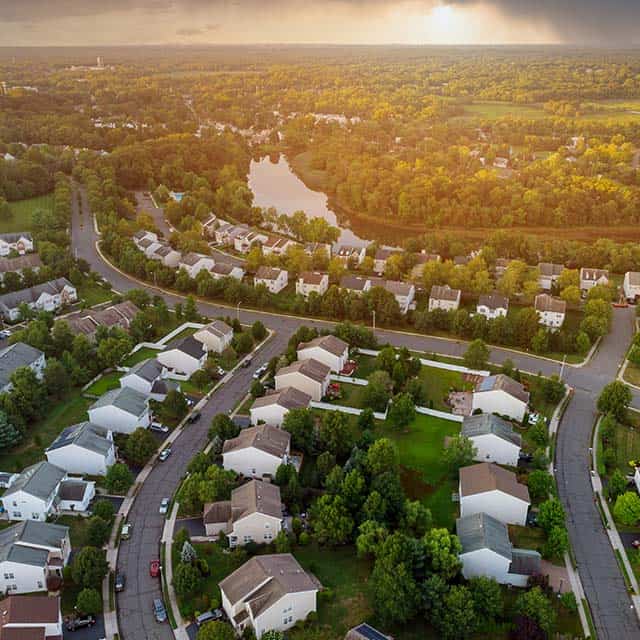
Real Estate and Land Management
GIS provides valuable insights for real estate developers, land managers, and local governments.
- Property Valuation: GIS integrates location data with market trends, zoning regulations, and infrastructure development to assess property values accurately.
- Land Use Planning: GIS helps governments and developers plan for residential, commercial, and industrial zones, balancing growth with sustainability.
- Environmental Impact Assessments: Before developing land, GIS assesses the potential environmental impact, helping to protect sensitive ecosystems.
- Smart Cities Development: GIS plays a crucial role in designing smart cities by integrating data on traffic, utilities, public services, and environmental factors for efficient urban management.

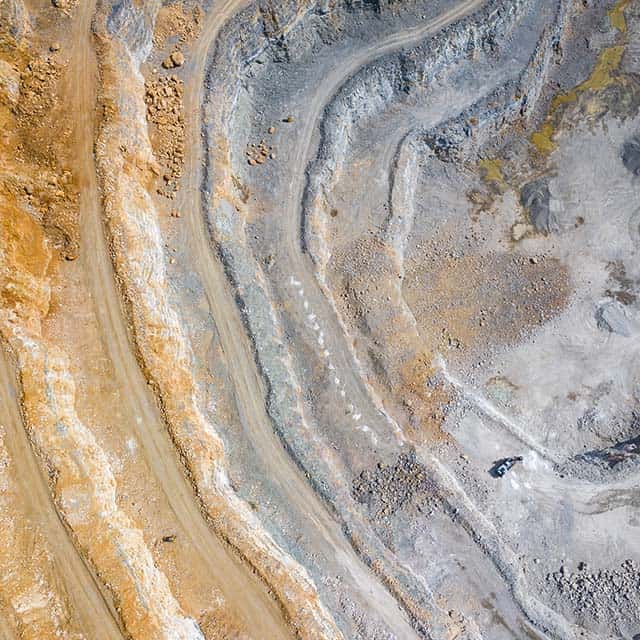
Mining and Natural Resources
GIS optimizes resource exploration and extraction while minimizing environmental impact.
- Resource Exploration: Mining companies use GIS to locate deposits of minerals, oil, and gas by analyzing geological data and satellite imagery.
- Environmental Compliance: GIS helps ensure mining operations comply with environmental regulations by monitoring land use, water quality, and biodiversity.
- Operational Efficiency: By mapping mine layouts and monitoring equipment, GIS enhances productivity and safety.
- Reclamation Planning: After resource extraction, GIS aids in planning land reclamation and restoration efforts.

Healthcare and Public Health
GIS contributes to improved healthcare delivery and public health outcomes.
- Epidemiology: GIS tracks disease outbreaks and models their spread, helping public health officials allocate resources and implement containment measures.
- Healthcare Access Analysis: By mapping healthcare facilities and demographic data, GIS identifies underserved areas and guides the placement of new clinics or hospitals.
- Emergency Services: GIS supports emergency response by mapping the fastest routes to hospitals and tracking the location of ambulances in real time.
- Health Risk Mapping: GIS visualizes data on pollution, water quality, and other environmental factors to identify communities at risk for health issues.
The Benefits of GIS for Businesses
Improved Decision-Making
By providing a clear, data-driven view of spatial environments, GIS empowers businesses to make informed decisions quickly.
Cost and Time Efficiency
GIS reduces the need for costly, time-consuming fieldwork by enabling remote data collection and analysis.
Enhanced Collaboration
GIS platforms allow multiple stakeholders to access and interact with the same data, fostering better communication and collaboration.
Risk Mitigation
Predictive analytics and real-time monitoring help identify potential issues early, reducing risks and avoiding costly setbacks.
Scalability and Flexibility
GIS can adapt to projects of any size, making it a valuable tool for industries ranging from local land management to large-scale infrastructure development.

