
Your GIS Is Only as Smart as Your Data Source
When it comes to Geographic Information Systems (GIS), one truth stands above all: your outputs are only as good as your inputs. No matter how sophisticated your software or how advanced your analysis tools, if your data is incomplete, outdated, or inaccurate, your results will also be flawed.
As Darian Bouvier, FlyGuys’ GIS Analyst, put it simply: “Data is everything. It’s the backbone of every map or model. No GIS tool can make up for bad or missing data.”
This principle drives the work of the FlyGuys GIS team, which integrates high-quality drone data into GIS platforms to help organizations accurately see, understand, and act on the world around them.
The Foundation: Why Data Quality Matters
At its core, GIS is about mapping and visualizing spatial relationships. Whether it’s a construction site, a floodplain, or a utility corridor, GIS turns raw location data into something meaningful. But that transformation depends on one critical factor: the quality of the source data.
“Poor or incomplete data can lead to inaccurate analysis and incorrect insights,” explains Matthew Berry, GIS Manager at FlyGuys. “You might make decisions based on faulty information, and that’s where things get costly. We see it all the time, a reflight, a redraw, or a rework because the foundation wasn’t solid.”
That’s why every successful GIS project begins with a strong data collection process. Drone-captured data, when properly collected and verified, provides the accuracy and freshness needed to build reliable models and maps.
From Traditional GIS to Smart GIS
So what does it mean to have a smart GIS?
According to Berry, it’s about transforming data into insight. “Smart GIS is like a smartwatch,” he says. “It delivers insights you didn’t even know you needed. It’s not just showing the data; it’s making it actionable.”
Modern GIS platforms combine automation, AI, and real-time integration to process massive amounts of spatial data faster than ever before. But automation can only work if the data feeding it is clean and consistent.
Bouvier cautions that “automation depends entirely on consistent input. If your data is inconsistent, the automated tools will just carry that error forward. That’s why human quality control is still so important. People can catch things that automation can’t.”
The blend of automation and expert oversight is where FlyGuys focuses much of its energy, ensuring that drone data meets strict accuracy standards before it is ever entered into a GIS platform.

Integrating Drone Data into GIS Workflows
Drone data has revolutionized how GIS professionals capture and visualize spatial information. With today’s UAV and LiDAR technologies, teams can generate centimeter-level accuracy across large areas faster and more cost-effectively than ever before.
But integrating this data into GIS isn’t always straightforward.
“The biggest challenge is managing different file formats and software limitations,” says Bouvier. “AutoCAD, for example, has limits on the size of files it can handle. ArcGIS Pro and ESRI platforms can work with much larger datasets, but you still need to make sure everything is formatted correctly before importing.”
FlyGuys’ in-house team helps clients navigate this process, ensuring data is properly formatted, verified, and optimized for their specific GIS applications. This level of diligence prevents slowdowns, crashes, and, most importantly, misinterpretations of the data.

When Bad Data Goes Wrong
Even small inaccuracies can have big consequences. Berry recalls a project where a client’s elevation files didn’t align with their existing GIS models.
“Our data was accurate to our internal controls,” he explains, “but the client’s source data was outdated. It caused noticeable differences in their models. In other cases, we’ve seen projects using imagery captured too early or missing the area of interest altogether. That’s why clear communication and accurate collection are key.”
These experiences reinforce one central message: GIS insights are only as strong as the data behind them. The more precise, current, and complete the data, the more reliable the analysis will be.

Maintaining Data Integrity
Maintaining the trustworthiness of GIS data over time requires consistency, structure, and effective communication across teams. Large or distributed organizations often struggle to maintain uniform data practices, and that’s where metadata becomes invaluable.
Metadata, or “data about data,” is the invisible layer that tells you how, when, and by whom a dataset was collected. “Metadata is critical for traceability and client trust,” says Berry. “It allows clients to verify the data on their own time without having to rely solely on the GIS processor. When metadata is missing, it becomes hard to trust the dataset.”
FlyGuys maintains comprehensive metadata with every deliverable, ensuring clients have full transparency into how their data was captured and processed.
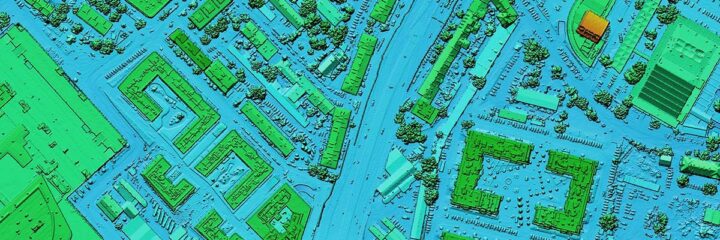
Best Practices for Building a Reliable GIS
For organizations transitioning from traditional mapping to data-driven GIS models, both Berry and Bouvier agree on one principle above all: start with good data.
“Good data in equals good data out,” Berry emphasizes. “Work with trusted partners and proven software. Don’t rush to automate everything. Get your foundation right first.”
Bouvier notes that partnerships and effective planning are crucial to achieving long-term success. “It takes time to structure your data properly,” she says. “But once that’s in place, everything else — automation, collaboration, visualization — becomes more efficient and reliable.”

Looking Ahead: The Future of Smart GIS
The next frontier in GIS is integration, connecting multiple data layers into a single, dynamic ecosystem. Berry predicts that collaboration and connectivity will define the future.
“We’re moving toward digital twins, all-encompassing models that integrate every data layer. Imagine an airport system that combines architectural, electrical, and environmental data into one live, constantly updating 3D model.”
Bouvier agrees, adding that improvements in accuracy and data management will continue to drive GIS innovation. “We’re seeing better tools, better collaboration, and better data integrity every year,” she says. “That’s where the industry is headed.”
The Takeaway
Your GIS is only as smart as your data source. Accurate, well-managed, and consistently verified data is what turns maps into insights and visuals into real-world decisions.
The path to smarter GIS starts with capturing reality as it is: clearly, reliably, and in detail.

