5 Industry Use Cases for LiDAR
LiDAR (light detection and ranging) is a rangefinding method which uses a laser that detects objects in real space with high precision and accuracy. The LiDAR instrument consists of a laser, scanner, and GPS attached to a drone, plane, or stationary platform. LiDAR emits pulses of light energy that scan the earth’s surface, creating points with coordinates in an x, y, and z-plane.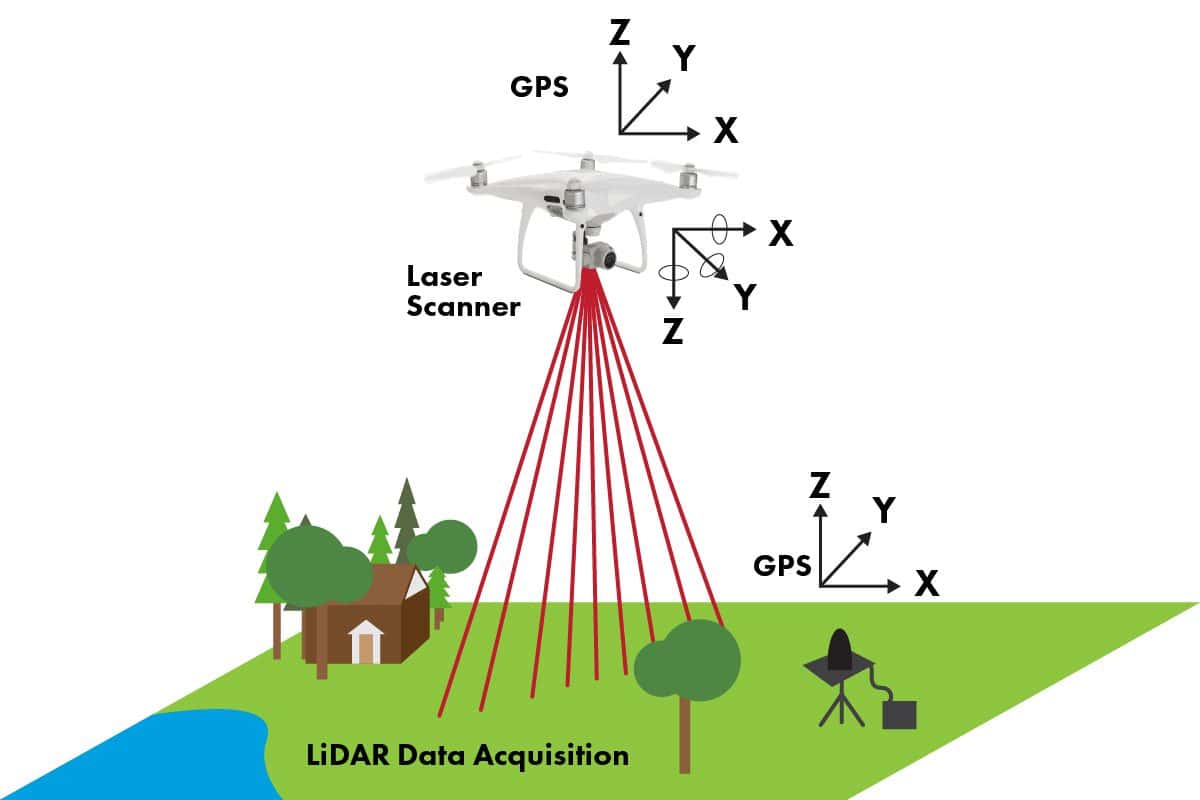

Civil Engineering & Surveying
Civil engineering and surveying projects are complex, and LiDAR is available to help streamline tasks. Civil engineers face budgetary constraints and must adhere to tight deadlines. LiDAR can help professional surveyors speed up delivery of certain project deliverables.Planning
Licensed professionals can use LiDAR to create Topographic deliverables. Civil engineers use this application in the planning stages of a project to see a three-dimensional landscape on a two-dimensional map, giving an in-depth and accurate picture of the land. Topo LiDAR also reveals comprehensive information about natural and manmade surface features of a region for urban planning.Design
LiDAR can create 3D models which can communicate design proposals and options to architects and stakeholders. A 3D rendering accurately visualizes the project and makes it easier to make design changes. LiDAR data can be shared using collaborative software to make communication between engineers, surveyors, project managers, and architects timelier and more efficient.Inspection
Civil engineers use LiDAR to inspect existing buildings for irregularities. Comparing previous data can identify structural changes that may be otherwise difficult to notice.Let Your Projects Fly
Drone services are driving cost and time savings across new industries every day. Find out how much your organization can save in this free download.
Construction
Using BIM technologies point cloud data from LiDAR can be used to determine project progress, which helps project managers budget the project more accurately.
Planning
For most construction projects, bare earth models are essential during the planning stage. LiDAR can create a bare-earth model by stripping back vegetation and existing structures to reveal the land’s topography. LiDAR can assess the terrain stability, identifying slope gradients and the risk of landslides and flooding in the proposed area.
Design
LiDAR data can create a 3D projection of the surrounding territory and create a realistic simulation of the new construction project in the existing terrain. Tests can show how the sunlight will reflect off the planned building to determine things like window size and shape.
Collaboration
Collaboration significantly improves with LiDAR, which means productivity is improved. Contractors are brought on board in the early stages, and LiDAR data is easily shared with people working in different industries on the same project. Data sets can be compared when an error arises or when sharing progress with team leaders.
Agriculture
Population growth has increased the demand for agriculture, and LiDAR is a valuable tool to increase yields and closely monitor the land so that farmers can operate more efficiently. LiDAR provides data that farmers can analyze to model and predict crop growth through topographic prediction of soil production.

Planning
LiDAR helps map out where farmers should plant certain crops to get the best sun exposure and water drainage while best protecting against erosion. This helps with loss prevention of produce and allows for maximum vegetation growth.
Crop control and 3D elevation mapping
LiDAR can help locate the most viable area on the farm where crops may flourish better than other farm areas. Finding these areas saves money on fertilizer and the time it takes to plant and prevents replanting dying crops.
Minimizing Erosion
LiDAR can detect minuscule shifts in the land, minimizing soil erosion that can be detrimental to crops. LiDAR allows farmers to adjust their planting locations to avoid losing valuable topsoil.
Energy
The power grid constantly expands, and long-distance power lines often run through mountainous regions. Daily inspections are required to locate new areas for development and to maintain existing power lines. LiDAR has a unique advantage in completing these job as it is one of the least expensive line inspection methods.
Planning
LiDAR can gather a high quantity of information in minutes, making it ideal for cellular infrastructure planning. LiDAR can help determine the line of sight for the proposed cellular antenna and create wireless signal mapping. It can tell cellular companies where the wireless transmitters should be positioned and can assess the strength and radius of the signal.
Maintenance
LiDAR point clouds and 3D maps measure the distance between foliage and power lines, which helps predict the areas that may become problematic to the utility network. LiDAR can also measure wire profiles allowing grid operators to locate and fix sagging power lines.
Inspection
Most daily inspections are conducted by electrical engineers using traditional ground-based observation methods or photogrammetry. These old-school methods have obvious limitations and safety risks. The speed of LiDAR inspections means measurements are gathered in seconds, allowing rapid inspection in an industry with high workloads and a constantly growing expectation for higher quality measurement.
Highway Development
LiDAR technology drastically reduces safety risks when developing or working on roads by keeping personnel away from traffic. It allows lanes to stay open in the early stages of a project and collects more ground data in less time than traditional methods take.
Planning
Field workers can use LiDAR to take lane and shoulder width measurements without physically being in the road near moving traffic. Engineers can use the technology to create a 3D model to plan accordingly in an expedited time.
Maintenance
LiDAR can detect shifts in the road before deterioration worsens. Before, patrol cars equipped with cameras would have to assess road upkeep, but the images were unidirectional and recorded only once.
Design
LiDAR can be used to help create the road design for a stable road and minimize the impact of new road constructions and maintenance.
Will Your Company Create the Newest LiDAR Use Case?
The many benefits of LiDAR make this technology the wave of the future, helping commercial industries worldwide become more efficient and successful. Contact FlyGuys today to explore how LiDAR measurement can transform your business processes, no matter your industry.